Polystyrene is one of the most widely used kinds of plastic. It is a polymer made from the monomer styrene, a liquid hydrocarbon that is commercially manufactured from petroleum by the chemical industry. Polystyrene is a thermoplastic substance; it melts if heated and becomes solid again when cool.
Polystyrene is most commonly found in three forms. Rigid Polystyrene (PS), Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS).
Rigid polystyrene has many applications, including disposable cutlery, CD cases, video/cassette casings, components for plastic model toys as well as some margarine and yoghurt containers. Extruded polystyrene foam has good insulating properties, making it important as a non-structural construction material. XPS is sold under the trademark Styrofoam by Dow Chemical; however, this term is often used informally for other foamed polystyrene products.
How to produce foam?
Expandable Polystyrene / EPS:
This is PS Foam that uses Pentane gas (C5H12) as the blowing agent. During the material production process called “Polymerisation” the polystyrene resin granules are impregnated with the blowing agent. EPS production processes begin in the pre-expansion process, where the EPS bead will expand by the heat of steam usually 50 times in volume. The next step in the process is moulding process, where the expanded foam bead will be heated again with steam, then they expand further until they fuse together, forming as foam products.
- Shape moulding machine that produce various shapes of foam products according to the molds such as icebox, helmet and packaging foam.
- Block moulding machine that produce block foam and sheet foam Expanded EPS foam bead contains 98% air per volume, only 2% is plastic. This make EPS foam very light weight, has low thermal conductivity because air is the best insulation, high compressive strength and excellent shock absorption. These properties make EPS to be ideal material for packaging and construction.
Polystyrene Paper (PSP):
This is a PS Foam which is produced by extruding process as another plastic. Production process start when put polystyrene resin pellets into the extruder that heated by electric. Foaming process occur at the end of extruder where the blowing agent, butane (C4H10) gas react with the melt plastic then become foam. The melted polystyrene foam is then extended as sheet then rolled as paper roll, that is why it is commonly known as “Polystyrene Paper”. The polystyrene foam sheet or polystyrene paper can be produced as many shape according to the mould by thermal forming process such as food tray, cups, bow, and food box.
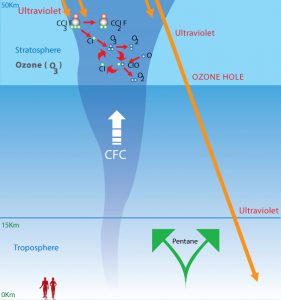
There’s no any CFC’s in PS foam
Both EPS and PSP contain 95 -98 % air another 2-5% is polystyrene which is pure hydrocarbon. CFC’s is Chlorofluorocarbons which is totally different in its chemical structure from polystyrene. CFC’s has very low blowing point and uneasy to be maintained in EPS beads. Therefore, EPS Foam never use CFC’s at any stage of its production. The blowing agent used since EPS Foam was first introduced in 1952 by BASF is Pentane gas which, does not contain any chlorine atoms as CFC’s. PSP Foam in the beginning used CFC’s as blowing agent. In the past two decades CFC’s are gradually phased out from plastics and refrigerator industries. PSP moulders in Thailand already use Butane (C4H10) as the blowing agent since the last 15 years. Butane gas is the gas that we use at home for cooking. The blowing agents that use in producing PS Foam are Pentane and Butane, which are pure hydrocarbon as polystyrene. They belong to the same chemical family, the paraffin series as methane, ethane, and propane gas.
How to manage the EPS foam waste
Apart from recycling by melting and compacting, there are many ways to manage the EPS waste as the followings:
- Crush in to small particle and mix with soil. Foam waste will improve ventilation in the soil, organic substances in the soil will become easier the humus.
- Mixing the crushed bead with cement to reduce the weight and increase insulation properties.
- Combustion at 1000 C with sufficient air supplies in to generate heat. Burning EPS require no any additional fuel, in fact EPS can replace the fuel normally required for combustion, l kg of EPS saves 1 kg = 1.2 – 1.4 Litre of fuel oil.
The Recycling of PS:
Since both EPS and PSP Foam are made of Polystyrene, which is thermoplastic, so that it will become again a polystyrene plastic when recycled. AMEPS members recycle both EPS and PSP Foam by first crushing into small particle then melting or compacting it. Melting can be done by heated roller, disk or screw extruders, where the regrind scraps is heated usually by electrical power for some time above the melting temperature. Compacting can be done by rotary compactors where pressure and frictional force create heat below melting temperature to soften the regrind scraps for only few seconds. This method also called “agglomeration”.
Magic EPS Recycling OVEN
Improved paddle for mixing
Improved pouring/casting


Plastic Planters

Pavement made from PS waste foot
Catwalk, Board, Synthetic timber plank




Easy Ways To Recycle EPS
Feeding of waste EPS


Setting of temperature 160c


Removal of mould from the machine